Madison’s lumber prices index is created Using the same species/product mix as Lumber Futures trading on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange
This two-year graph below shows these concurrent data sets correlate very nicely:
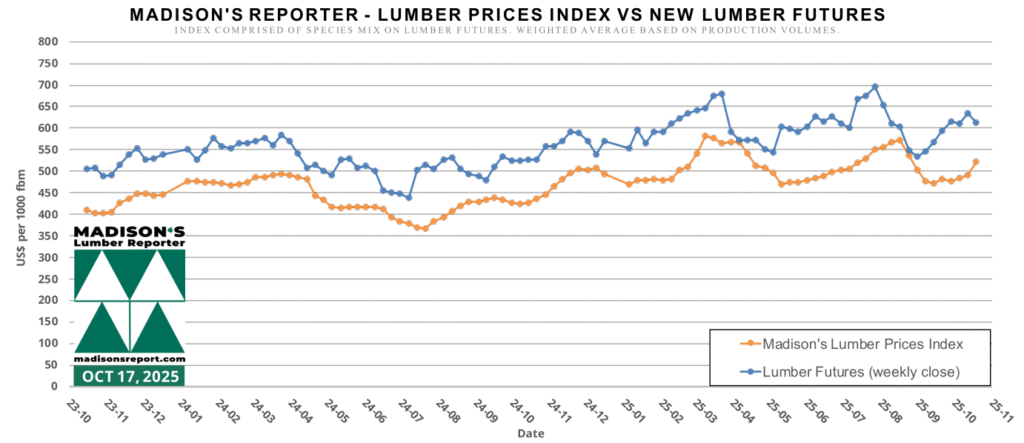
Madison’s Lumber Prices Index can signal upcoming changes and broad trends in the economy, which has tremendous value when examined across a period of time.
This graph demonstrates a reliable symmetry between prices of Futures and that of cash sales for manufactured solid wood products across North America than there was in the past. The spot price of a commodity is the current cash cost of it for immediate purchase and delivery. The futures price locks in the cost of the commodity that will be delivered at some point other than the present—usually, some months hence.
An index tracks the price of an asset. A futures contract is a derivative that obligates traders to buy or sell the underlying asset on a set day at a predetermined price.
Commodity futures allow traders to buy or sell a specified amount of a commodity at an agreed-upon price on an agreed-upon date in the future. Investors generally trade commodity futures to hedge or speculate on the price of the underlying commodity.
